A tangible object can be created via 3D printing from a digital model.
Up until the object is finished, successive layers of a material, such as plastic or metal, are laid down to construct the object. The digital model is divided into thin layers, each of which is printed separately to create the object layer by layer. Additionally referred to as additive manufacturing, this process.
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), which is an extrusion-based process in which the material is melted and extruded through a nozzle to make the object, is the most popular 3D printing technique.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), which utilises a laser to fuse tiny material particles together, and Stereolithography (SLA), which employs a laser to cure a liquid resin, are two more common 3D printing techniques.
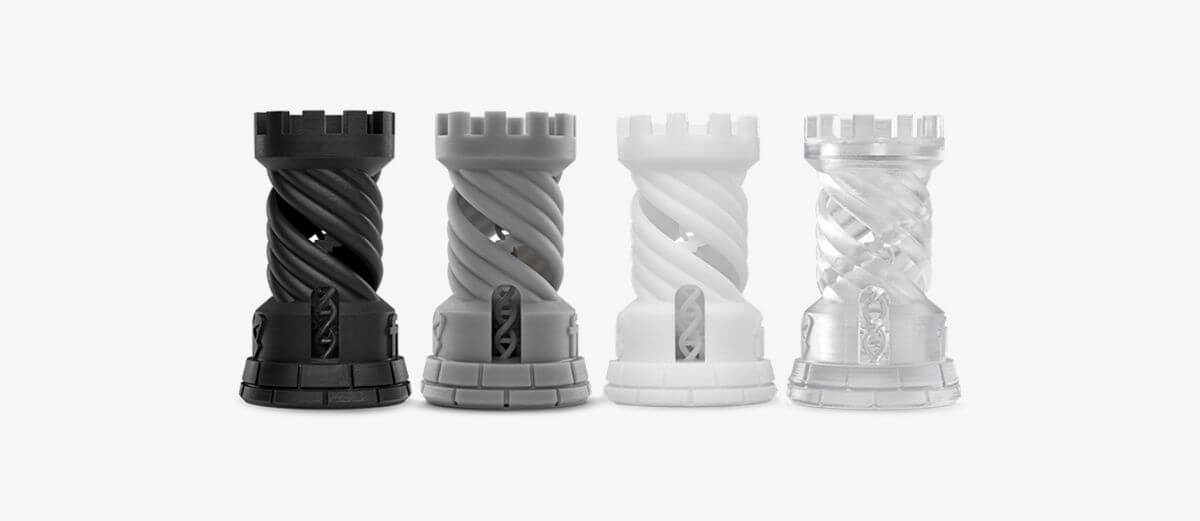

Another name for 3D printing is additive manufacturing. Instead of removing material from a block of material, it refers to the process of producing an object by adding subsequent layers of material (subtractive manufacturing). Due to its ability to produce prototypes and limited quantities of goods quickly, this approach is also known as “rapid prototyping.”
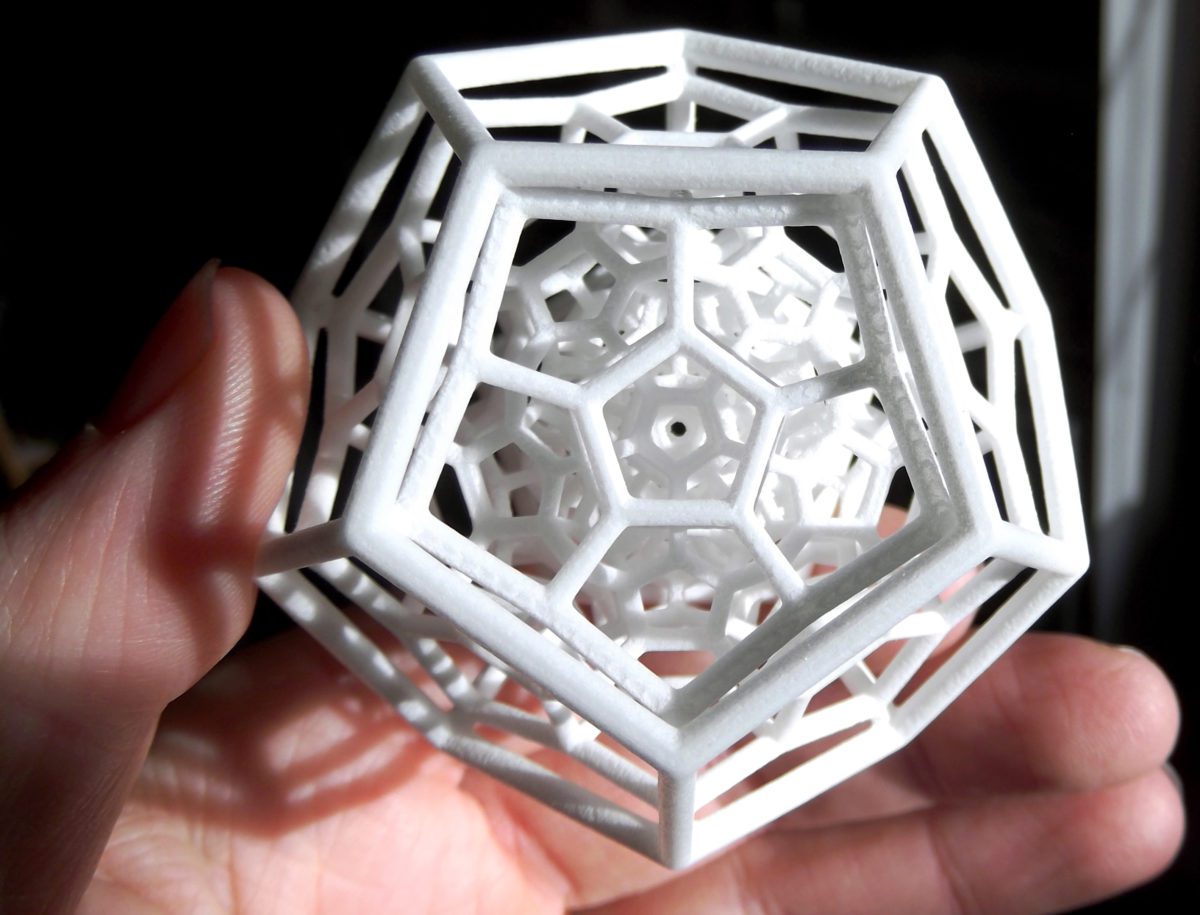
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) are just a few examples of the numerous types of additive manufacturing techniques available, each of which uses a different set of tools and processes to produce items.
Complex geometries, interior structures, and functional pieces that are impossible to fabricate using conventional manufacturing techniques can now be made with this technology.
3D Printing can be used in a variety of industries. Take a look at some sectors that are already taking advantages of this amazing technology;
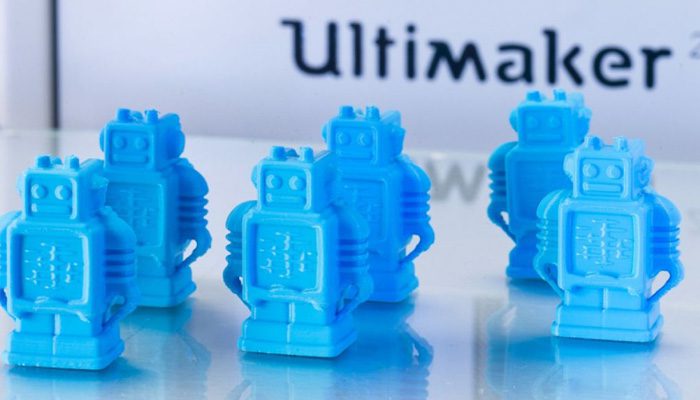

In general, 3D printing is a rapidly developing technology that could disrupt a wide range of sectors and alter how we live and work. Begin with the fundamentals;
3D APAC Pty Ltd Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved